 The needle you use in your sewing machine can make the difference between perfection and a disaster. Use the wrong needle, a damaged needle or a worn needle and you could end up with broken threads, holes, uneven stitches, puckers and possibly even permanently damaged fabric. To keep your seams straight and your collars curvy, there are several points to successful stitching.
The needle you use in your sewing machine can make the difference between perfection and a disaster. Use the wrong needle, a damaged needle or a worn needle and you could end up with broken threads, holes, uneven stitches, puckers and possibly even permanently damaged fabric. To keep your seams straight and your collars curvy, there are several points to successful stitching.
Check first
Check for any special requirements for your specific machine. For the most part, standard sewing machine needles can be used in any sewing machine. However, differences may be found in some machines like sergers, embroidery machines and some brands which could require a special needle.
Size matters
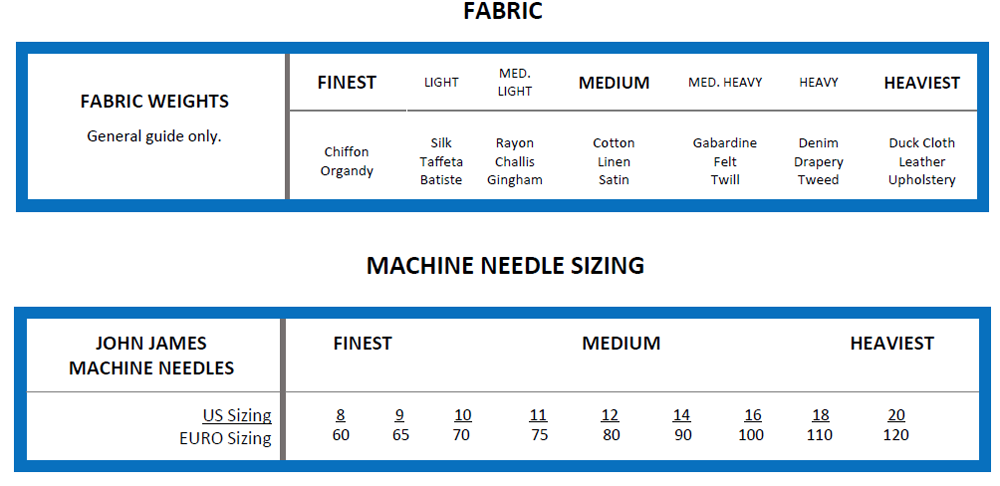
Needle size is the numeric representation of the diameter of the blade. Note that when you see needle sizes, they are labeled with two numbers, separated by a slash (65/9, 80/12, etc.). This refers to EURO metric sizing (in millimeters) and the comparable US sizing. The following chart from Colonial Needle describes the fabric weights and the size of needle that are appropriate for each project.
ASG Members receive a 20% discount. See the Special Offers page in Members Only.
Download the Colonial Needle machine needle resource guide.
 Let’s Get to the Point
Let’s Get to the Point
- There are 3 basic General Purpose needle types. Universal needles are usually used in knits and wovens. Ball points are great for knits. Finally, Sharps/Microtex are used in finely woven fabrics.
- Specialty needles are available for use in denim, leather, embroidery, metallic (for use with metallic threads), quilting, twin, triple, stretch and more. Check out this Guideline for an extensive list of needle types, sizes and their uses.
Needle Tips
- For best results, needles should be replaced every 6-8 hours of sewing time.
- If you hit a pin, even if the needle seems okay, it’s safer to replace it.
- Needle breakage could mean that the needle size is too small for the type or thickness of fabric you are using. In this case, try changing to a larger needle size.
- When you are sewing, allow the feed dogs to draw your fabric along. Use a light touch with your hands to guide the fabric rather than pushing or pulling, which could cause your needle to bend and break.
Stock up
It can be frustrating to not be able to start — or finish — a project because you don’t have the correct needle or don’t have a replacement, so make sure to keep a good supply of your favorite needles on hand. ASG members can take advantage of a 20% discount on needles, notions, thimbles, thread, jewelry and more at Colonial Needle by visiting the Special Offers section of ASG.org
~Janice Blasko, webgoddess for ASG











 Different types/brands of interfacings require different fusing techniques, so be sure to read the label. Some require steam, others dry heat, while still others specify a damp press cloth. Note the fusing time and iron temperature for proper adherence.
Different types/brands of interfacings require different fusing techniques, so be sure to read the label. Some require steam, others dry heat, while still others specify a damp press cloth. Note the fusing time and iron temperature for proper adherence. Wool or a wool blend is the best choice for a tailored garment, as it’s easily shaped with steam and good pressing techniques. Preshrink your wool selection prior to sewing—easily done by asking your dry cleaner to steam press it for you, though some wools are washable, so check the label first.
Wool or a wool blend is the best choice for a tailored garment, as it’s easily shaped with steam and good pressing techniques. Preshrink your wool selection prior to sewing—easily done by asking your dry cleaner to steam press it for you, though some wools are washable, so check the label first.


